The Center attained a record number of patents, finding new ways to involve the top-level research conducted in partnership in benefits for society, and absorbing each demand as a challenge.
PARTNERSHIP
SUPPORTING INNOVATION

Activities in the area of Innovation at CNPEM are organized into four fronts:
In 2020, CNPEM broke its record for intellectual property protection, which contributed to the Center’s first appearance in the ranking of the top 50 Brazilian organizations that filed the most patent applications with the National Institute of Industrial Property (INPI) that year. CNPEM’s objective in protecting intellectual property is to be judicious and protect only technologies with high market potential, in order to allow transfer to companies and use by society.
Although industrial contracting of new R&D projects has slowed during the pandemic period, due to uncertainties about economic recovery and retraction, CNPEM have made more approaches to startups and in diversification of partner companies. The Center has also established cooperation agreements with three startups in the field of biotechnology applied to health.
Check out the current Technological Showcase for CNPEM’s Innovation Support area, and contact the Innovation team at inovacao@cnpem.br
TECHNOLOGICAL WINDOW

BIOPRODUCTS
Converting macauba oil into bioproducts
The process of converting macauba oil using a lipase to produce biohydrocarbons uses raw materials from a renewable source; advantages include resistance to organic solvents, acidic environments, and high temperatures.

One adhesive,
different solutions
This water-based contact adhesive formulated from renewable raw materials can be used on different types of substances and allows adhesion between them (such as metal, wood, paper, and polymers, for example). Not only is it free of organic solvents, it does not require temperature or pressure curing.

Biocharcoal-based fertilizer
This biofertilizer made from biomass supplements, adjusts, balances, and replaces nutrients gradually and keeps moisture in the soil for a prolonged period.
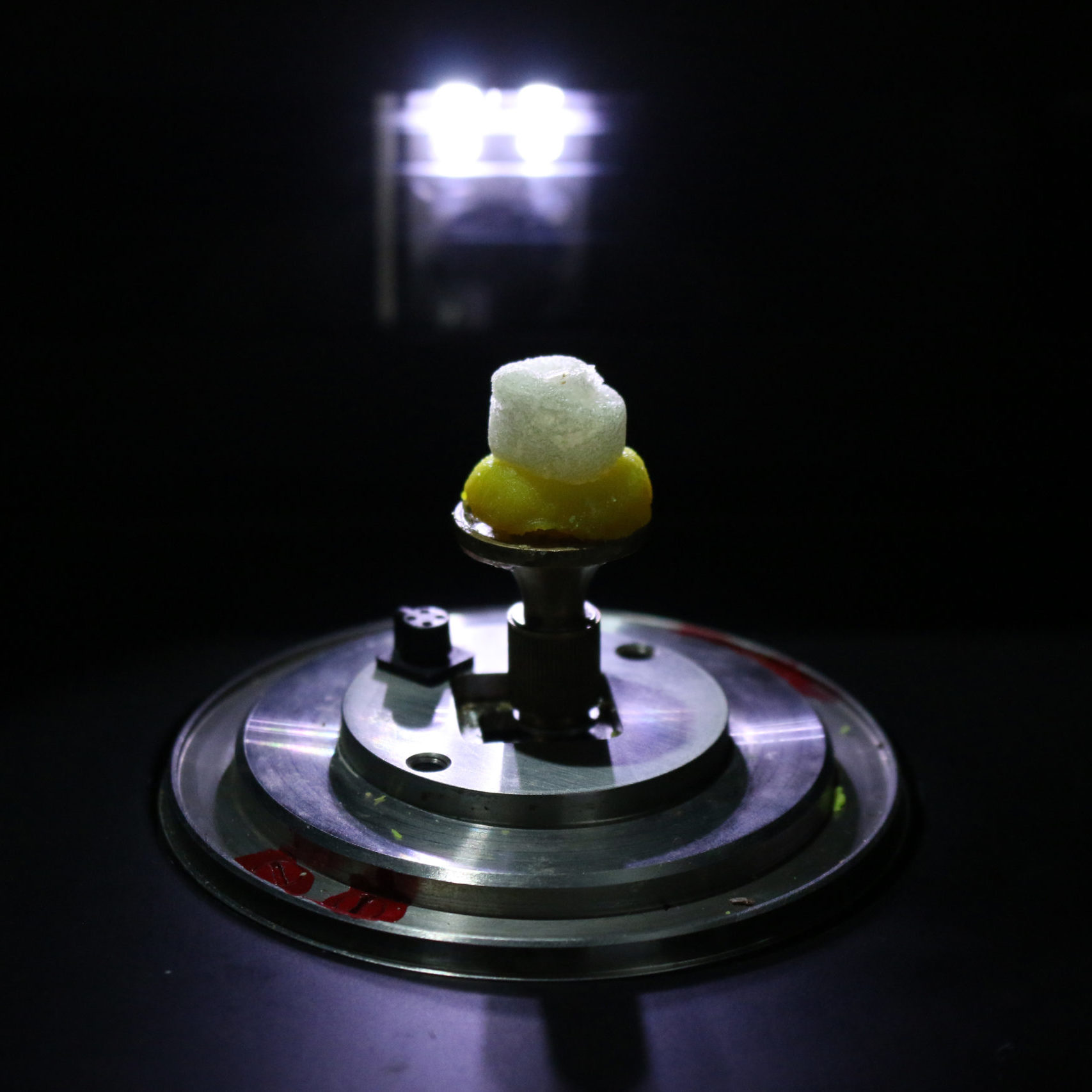
Green foams
These environmentally friendly foams are formulated from renewable raw materials for environmental decontamination, with rapid absorption of different aromatic compounds, such as organic solvents, silicones, vegetable oils, or synthetic oils.

Enzymatic method for preparing monounsaturated alkene
This enzymatic process to prepare monounsaturated alkene from a peptide with a fatty acid can generate alkenes to use in the production of biofuels, intermediates, and biochemicals. The main advantage is lower cost, since enzymatic activity occurs at a wide range of temperatures and pH levels, allowing the use of only one conversion step.

ETHANOL
Enzyme cocktail for 2G ethanol production
Enzyme cocktail production onsite method for second-generation (2G) ethanol production. It is a sustainable method since it uses waste from production, such as bagasse and straw sugarcane. The performance is approximately 50% higher than imported trade options.

ENVIRONMENT
Enzymatic cocktail
for to degrade plastics
This enzymatic cocktail to decompose polymers is resistant to high temperatures and does not require concurrent use of additional enzymes. The use of this compound favors the circular economy; it may be applied in various areas, including waste and effluent treatment and recovering precursors to synthesize new polymers in different segments of the industry.

CONDUCTORS
Sustainable conducting material for heating and sensor applications
This bamboo microreactor is capable of performing various types of organic reactions, and is produced using renewable, low-cost raw materials.
CELLULOSE
Bioglass
Compound made of bioactive glass and cellulose induces bone growth. Not only is it biocompatible, but it also offers appropriate mechanical properties for application in inducing bone regeneration to treat injuries. It is made from renewably sourced raw materials.
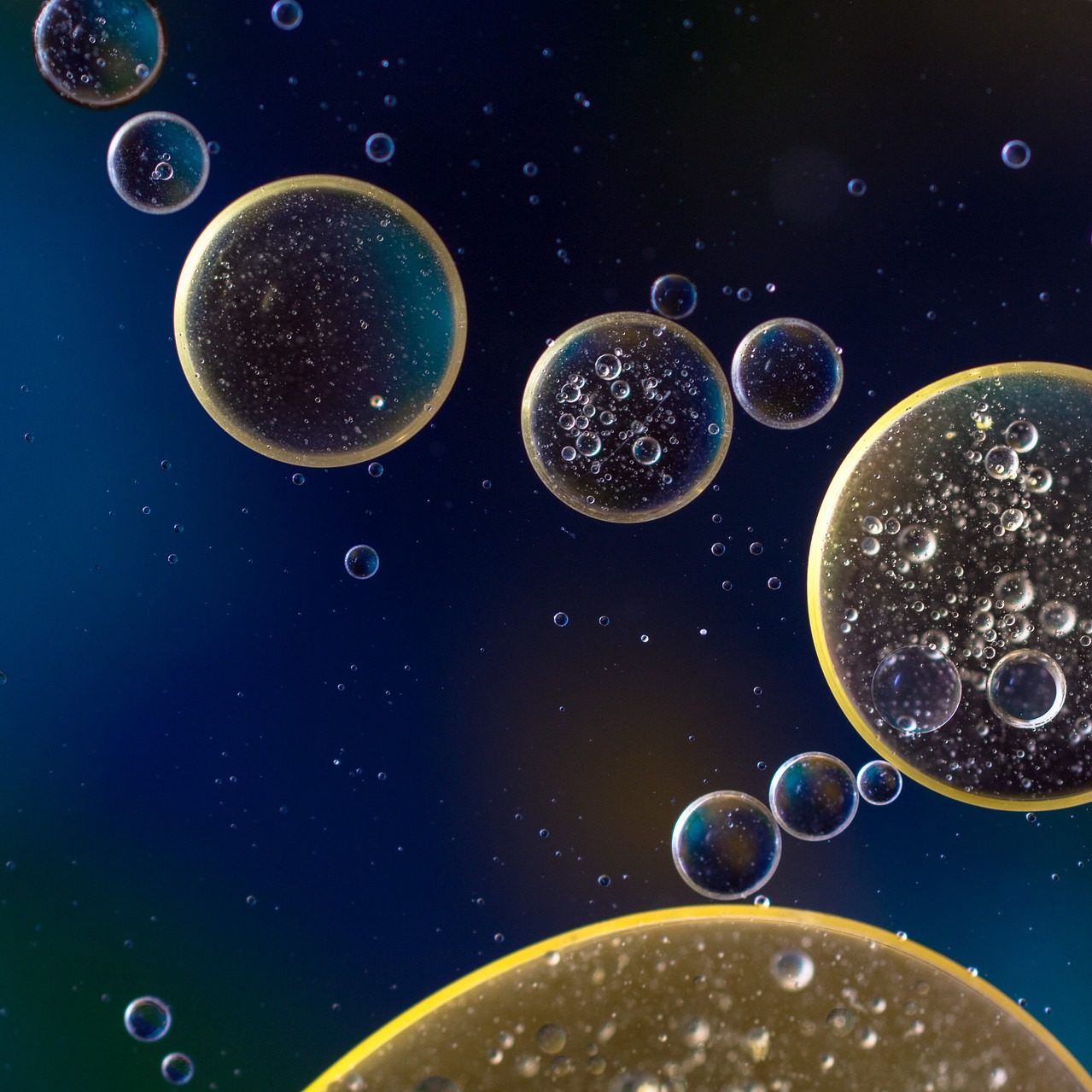
Emulsion with nanocellulose
This nanocellulose-based physical agent produced from renewable raw materials to stabilize emulsions with different proportions of water and oil offers broad potential for applications in the cosmetics, pharmaceutical, and food industries.

Process of producing
nanofibrillated cellulose
This process of obtaining nanofibrillated cellulose from sugarcane bagasse without mechanical treatment involves lower energy costs related to mechanical processing, and yields material with unique nanoscale characteristics.
DIAGNOSIS
Chip for cancer diagnosis
Fast and highly sensitive testing equipment for diagnosing some types of cancer (such as breast cancer) using human blood serum. Not only does it permit rapid testing, it is reusable and economical to produce.

RESIDUES
Compound process for separating aromatics
This process for separating aromatic compounds from agricultural processing waste such as sugarcane bagasse potentiates characteristics of these compounds such as photoprotective, antioxidant, and immunomodulating properties that can be applied in industrial segments such as food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.

DISPOSITIVES
Miniature system for fractional distillation
This device for small-volume fractional distillation allows faster analysis, generates less waste, and also leads to savings due to the small amounts of sample required for analysis.
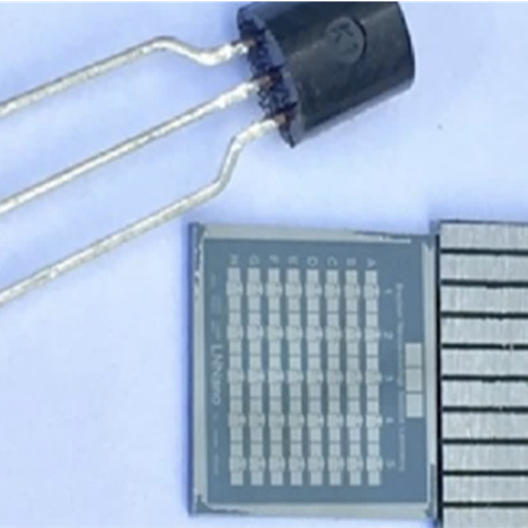
Vertical organic field-effect transistors (VOFET)
This device for use in vertical effect organic transistor-type sensors detects minimal differences in sensing parameters and allows the manufacture of flexible components.
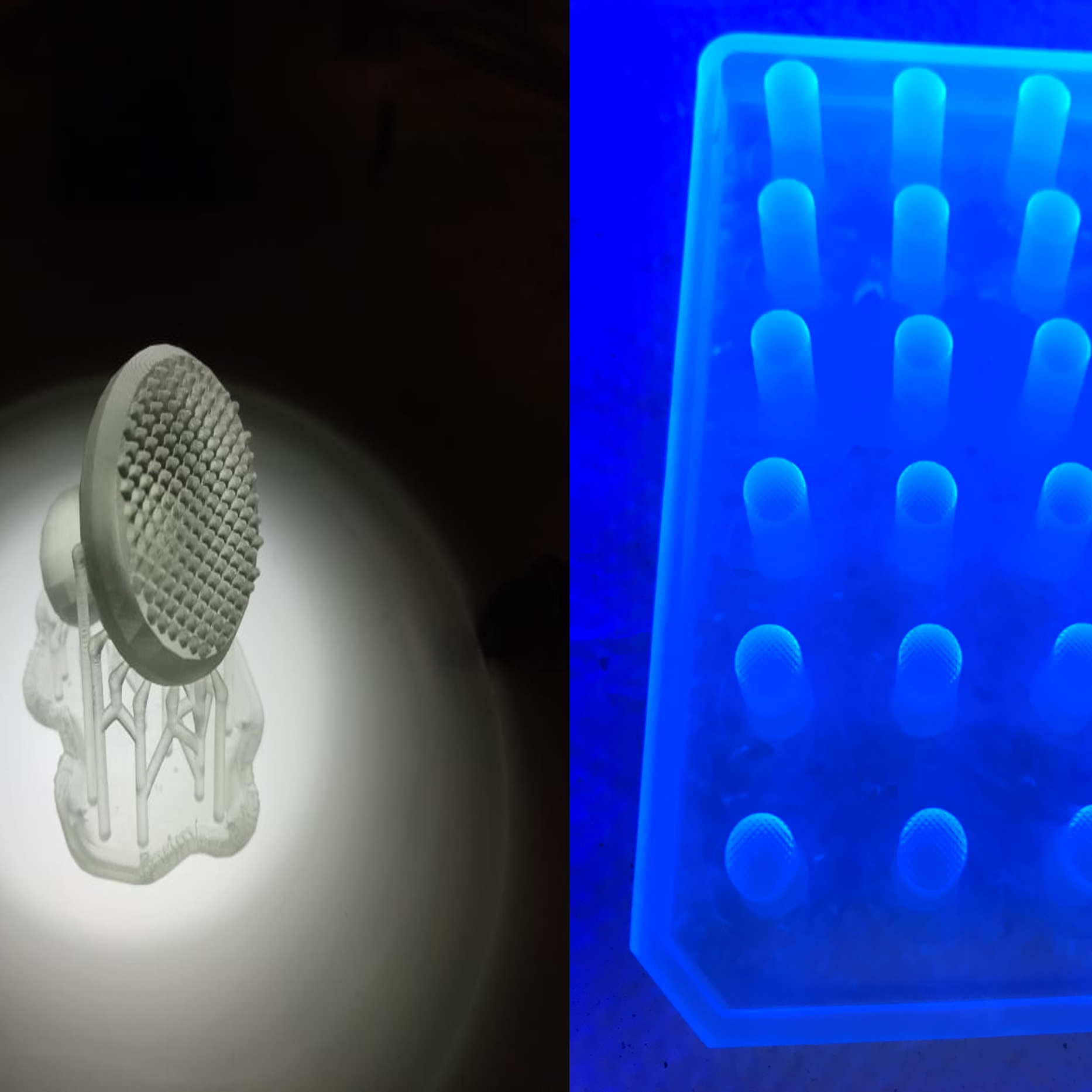
Micromold - Imitating the skin's surface
This easy-to build, reusable stamp-like mold transfers relief from biological tissues in order to promote cellular adhesion; it offers versatility in enabling the entire cellular growth process in a single step.
